Is There Microbial Life Under the Martian Surface?
Article by Lilia Dergacheva April 25, 2021 (sputniknews.com)
• Scientists diligently searching for signs of microbial life on Mars, or to be more precise – beneath the surface of Mars, studied the chemical composition of Martian meteorites that chipped off from the Red Planet and wound up falling to Earth. They found the Mars rock fragments to be similar to Earth’s rocks in composition. In Earth’s depths, scientists have discovered a vast population of sub-world creatures. Postdoctoral researcher Jesse Tarnas, of NASA’s Jet Propulsion Laboratory, says that wherever there is groundwater on Mars, chances are that there may be sufficient chemical energy to support subsurface microbial life.
• Due to a severe lack of sunlight, microbial species survive in the sub-surface due to a chemical process known as radiolysis. Radiolysis occurs when radioactive elements within rock come into contact with water in rock pores. This creates the chemical reactions that forms living microbes. The elements required for this process can be found in Martian meteorites. Meteorites formed from crustal rocks more than 3.6 billion years old, known as ‘regolith breccias’, have a high potential to support life.
• Previous research has already revealed an active groundwater system on Mars that could still exist today. A recent study even indicates that there is a hidden underground lake the southern ice cap. This sub-terrain water would provide ample energy to sustain life. Brown University Professor Jack Mustard noted that only a relatively small drill could access the Martian depths to investigate their theory.
• “We don’t know whether life ever got started beneath the surface of Mars,” says Tarnas. “[B]ut if it did, we think there would be ample energy there to sustain it right up to today.”
• [Editor’s Note] What will these heavily-controlled scientists say when they learn the truth, that indigenous life does indeed live underneath the barren surface of Mars? Underground Martian colonies contain fully developed populations insectoid races, reptilian races (not associated with the malevolent Draco reptilians), and ancient humanoid races. In fact, in Dr. Michael Salla’s recent series of videos and articles with French ET-contactee Elena Danaan, Danaan has revealed that the Galactic Federation of Worlds (a human extraterrestrial governing body that oversees this sector of the galaxy) is actively arming these indigenous Mars insectoids and reptilians to fight off the encroaching deep state elite from Earth that is operating over a dozen factory bases on Mars using slave labor, known as the ‘Interplanetary Corporate Conglomerate’ (according to Corey Goode), and the mercenary forces including former Nazi ‘Dark Fleet’ forces stationed on Mars to protect the corporate conglomerate bases.
For more on this, see Dr. Salla’s recent article, “Is Mars in the midst of a Planetary Liberation War?”, and his three previous Danaan articles, “Extraterrestrial Contact & the Galactic Federation”; “Update on Galactic Federation Attacks on Corporate Satellites & Mars Exodus”; and “Overview of Human-looking extraterrestrials & their agendas”.

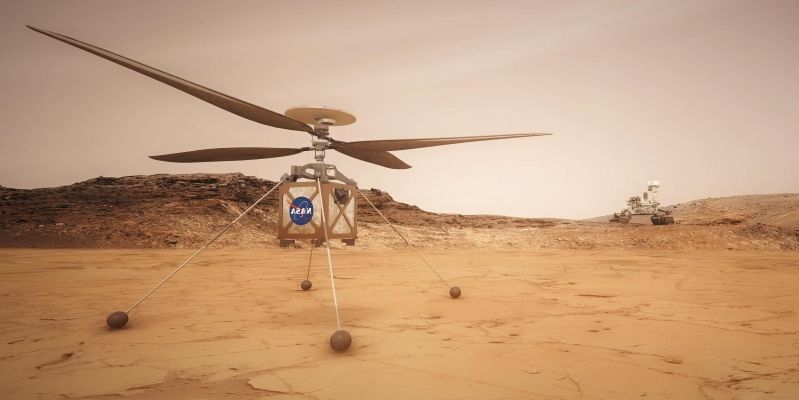
Scientists suggest that in the search of life on Mars they should go no further than

the Martian subsurface, currently being drilled by NASA’s Perseverance Rover, with the help of its helicopter Ingenuity.
Their latest study on the subject has been published in the journal Astrobiology.
It looked at the chemical composition of Martian meteorites that chipped off from the Red Planet’s surface eventually ending up on Earth, finding the fragments to be similar to Earth’s rocks in composition.

“We don’t know whether life ever got started beneath the surface of Mars but, if it did, we think there would be ample energy there to sustain it right up to today”, said postdoctoral researcher Jesse Tarnas, of NASA’s Jet Propulsion Laboratory.
He stressed that wherever there is groundwater on the Red Planet, chances are that there may be sufficient chemical energy to support subsurface microbial life.

As for Earth’s depths, scientists have in recent years discovered that they are home to a vast population of unique, sub-world creatures.
Due to a severe lack of sunlight, the species survive thanks to a chemical process known as radiolysis, which occurs when chemical reactions yield by-products of radioactive elements within rock while contacting with water in rock pores. Likewise on Mars: the Martian meteorites were found to have the same collection of elements needed for radiolysis, while they are also easily permeable to water.
This was particularly typical of regolith breccias, meteorites formed from crustal rocks more than 3.6 billion years old, which appeared to have the highest potential to support life.
FAIR USE NOTICE: This page contains copyrighted material the use of which has not been specifically authorized by the copyright owner. ExoNews.org distributes this material for the purpose of news reporting, educational research, comment and criticism, constituting Fair Use under 17 U.S.C § 107. Please contact the Editor at ExoNews with any copyright issue.
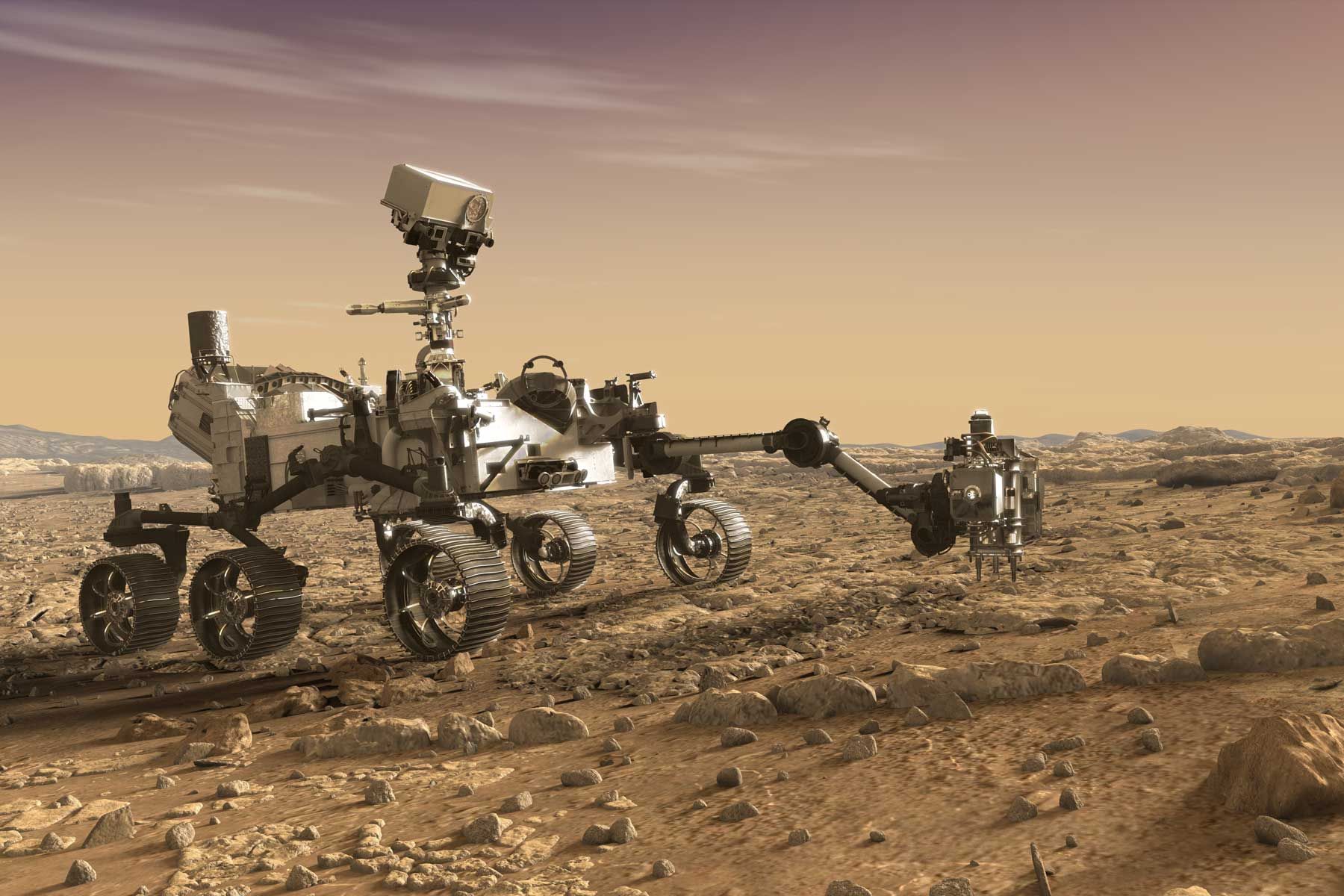


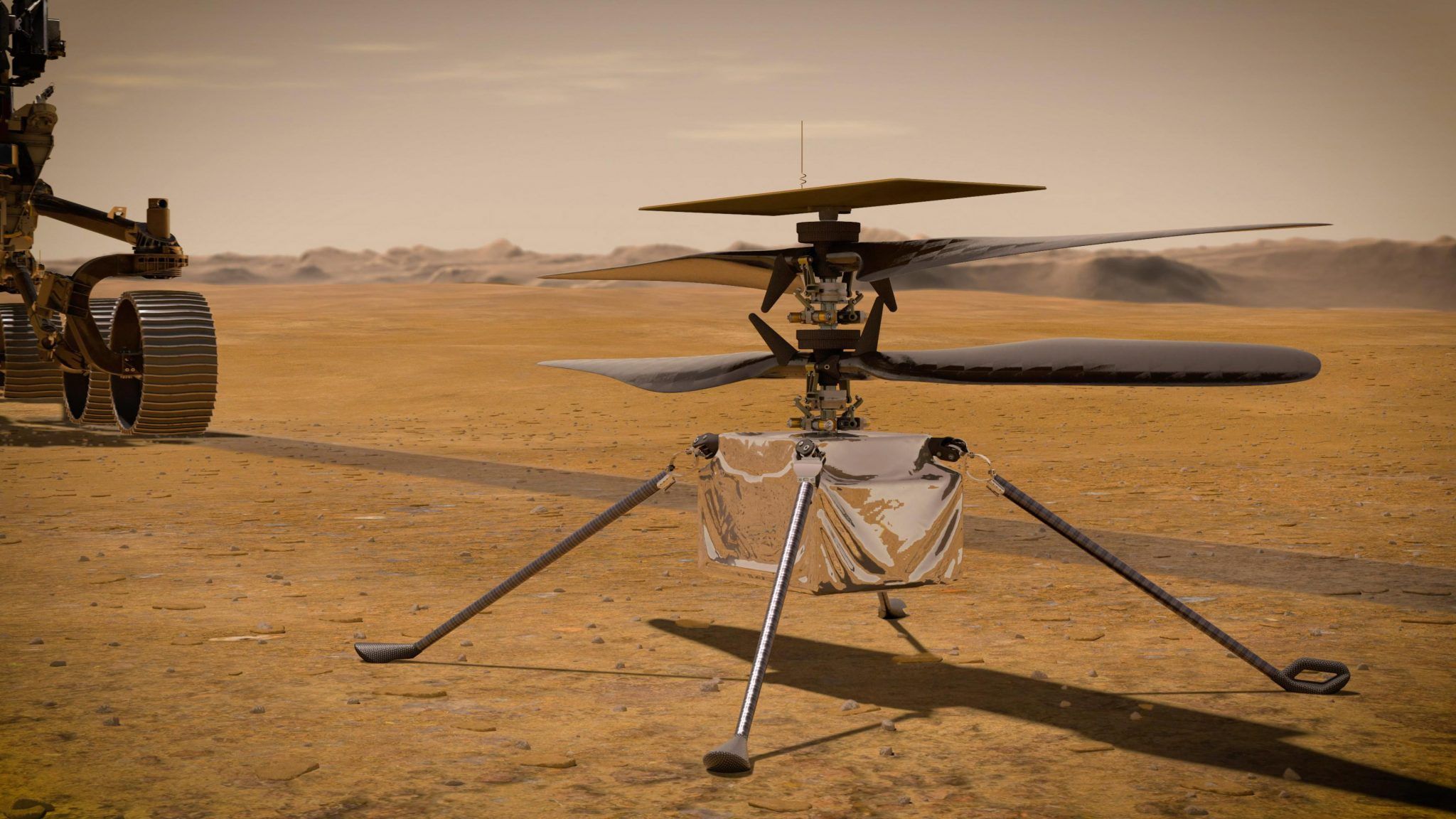
 NASA’s Mars 2020 Perseverance rover took its first test drive on Mars Thursday,
NASA’s Mars 2020 Perseverance rover took its first test drive on Mars Thursday,
 “When it comes to wheeled vehicles on other planets, there are few first-time events that measure up in significance to that of the first drive,” said Anais Zarifian, Mars 2020 Perseverance rover mobility test bed engineer at NASA’s Jet Propulsion Laboratory in Southern California.
“When it comes to wheeled vehicles on other planets, there are few first-time events that measure up in significance to that of the first drive,” said Anais Zarifian, Mars 2020 Perseverance rover mobility test bed engineer at NASA’s Jet Propulsion Laboratory in Southern California.






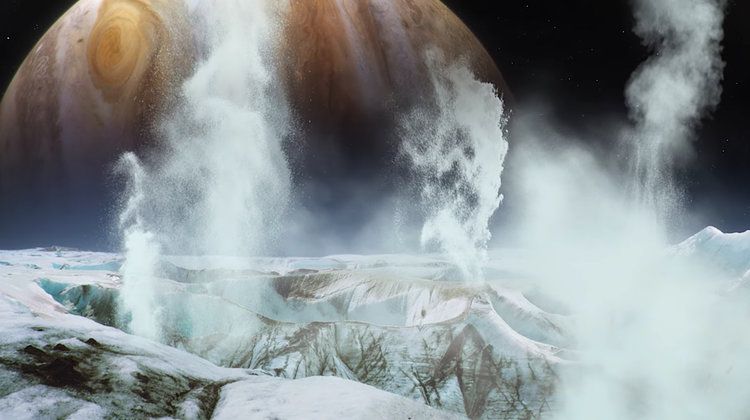
 NASA’s plans to explore the ice moons of the Solar System are getting more detail as the space agency is developing a robot that would use steam to power itself in deep space.
NASA’s plans to explore the ice moons of the Solar System are getting more detail as the space agency is developing a robot that would use steam to power itself in deep space.