German Scientists Create the First All-Sky Map of Millions of Black Holes
Article by DNA Web Team July 28, 2021 (dnaindia.com)
• A team of scientists at the Max Planck Institute for Extraterrestrial Physics in Germany has developed the first-ever detailed map of millions of black holes, supermassive black holes and neutron stars
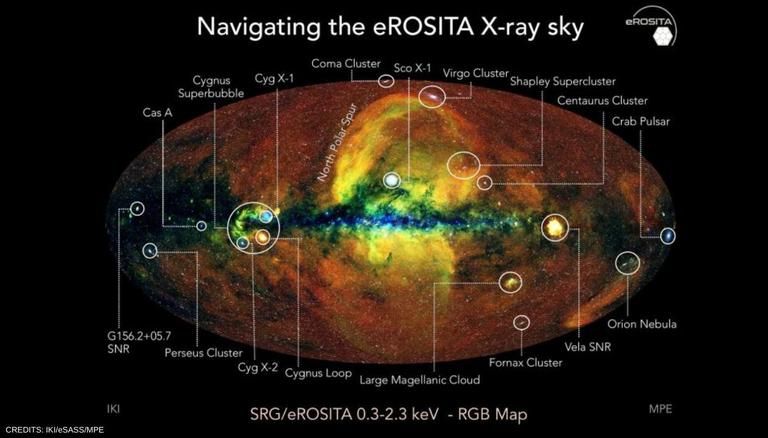
• The black hole map was created using data from the eROSITA observatory, the first space-based X-ray telescope that can observe the entire sky at once. Launched in 2019, the eROSITA is the main instrument of the Spectrum-Roentgen-Gamma mission which is a joint endeavour by Germany and Russia.
• The space observatory is positioned at the Lagrange point 2, one of five stable points in space where the gravitational pull of Earth and Sun is balanced. At this vantage point, the eROSITA captures images of the universe in clear view and has identified over 3 million previously unknown celestial objects.
• Other X-ray telescopes like NASA’s Chandra X-ray Observatory and the ESA’s XMM Newton are limited to only small sections of the sky in a single image. The eROSITA is the first X-ray telescope to image the entire sky. “Large survey optical telescopes are now quite commonplace because they are very useful to study cosmology [the evolution of the universe] and things such as dark energy. But optical telescopes are much easier to design than X-ray telescopes,” said Andrea Merloni, principal investigator for eROSITA.
• Some celestial entities like black holes and neutron stars do not emit light at visible wavelengths and remain invisible to the large field optical telescopes. These entities and even distant galaxy clusters, however, can be easily observed using X-ray telescopes. “The X-ray telescopes so far have been able to look very deep into the center to observe the early Universe,” says Merloni. “But it has always been very difficult to compile large populations [of black holes, neutron stars and clusters] and create a large catalogue that you could then use to study their cosmological evolution”

The first-ever detailed map of millions of black holes, supermassive black holes and neutron stars has

been developed by a team of scientists from Max Planck Institute for Extraterrestrial Physics in Germany.
The map has been created thanks to data from the eROSITA observatory, the first space-based X-ray telescope that can observe the entire sky at once. Launched in 2019, the eROSITA is the main instrument of the Spectrum-Roentgen-Gamma mission which is a joint endeavour by Germany and Russia.
The observatory is positioned at the Lagrange point 2 which is among the five stable points in space where the gravitational pull of Earth and Sun is balanced out. Sitting at this vantage point, the eROSITA captures images of the universe in clear view. In less than two years, the data has brought to light over 3 million previously unknown celestial objects.
 How eROSITA performed the imaging of the entire sky
How eROSITA performed the imaging of the entire sky
eROSITA is the first X-ray telescope to image the entire sky in a similar fashion to large field optical telescopes, several of which are in use around the planet.
As per Andrea Merloni who is principal investigator for eROSITA, “Large survey optical telescopes are now quite commonplace because they are very useful to study cosmology [the evolution of the universe] and things such as dark energy. But optical telescopes are much easier to design than X-ray telescopes.”
Nevertheless, some interesting celestial entities like black holes and neutron stars do not emit light at visible wavelengths. Thus, they remain invisible to the large field optical telescopes. Even distant galaxy clusters are much easier observed using X-ray telescopes.
FAIR USE NOTICE: This page contains copyrighted material the use of which has not been specifically authorized by the copyright owner. ExoNews.org distributes this material for the purpose of news reporting, educational research, comment and criticism, constituting Fair Use under 17 U.S.C § 107. Please contact the Editor at ExoNews with any copyright issue.
Andrea Merloni, black holes, Chandra X-ray Observatory, eROSITA observatory, Max Planck Institute for Extraterrestrial Physics, XMM Newton